PRACTICE ACTIVITIES AND TASKS FOR LANFUAGE AND SKILLS DEVELOPMENT

·
TeachingEnglish
| British Council | BBC
Free practice
·
Tesolcourse.com
Controlled Practice and Free Practice

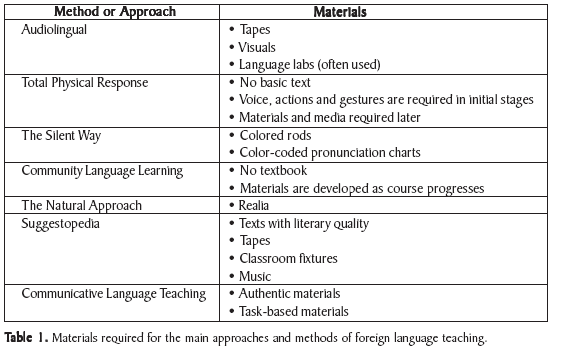
In this chapter, I learned some activities and tasks to gives pupils opportunity to practice
the use of language. These activities are: vocabulary, functional exponents
or grammatical structures, or of the subskills
of reading, listening, speaking or writing. Also we can find different kinds of
activities and task with different names and different uses. We categorized
activities into: controlled activities, free activities. Into controlled
activities pupil focus in accuracy and the form of the language, and allow students make few mistakes. They
are used to guide pupils in using the form of target language. Examples of controlled activities are:
copying words or sentences, jazz chants and drills. Drills are the most
essential activities that teacher can provide student in the class. It will be choral drill, individual drills, substitution drills (replace key words), and transformation drills. While
free activities are not controlled. These allow students to use the language
freely. Here teacher may not be able to predict what language the student will
use. These activities focus only in fluency. So, activities that help students
in their fluency are: discuss, debate, problem-solving activities, sharing or
comparing information, stories ect. The activities
that will be provided in class are going to be essential for students. In
addition, teachers choose different activities for students, it depend on what
is going to teach them, what she o he is going to achieve with students.
This video show differents controlled activities that teacher use in the class.
References